Lesson 1: Parts of a Plant
Additional Resources
Objective
- Students will understand the parts of a plant and what they do.
Background
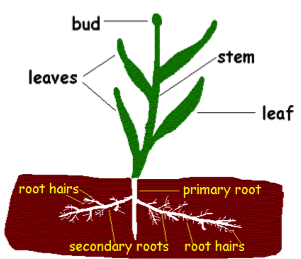
Plants come in different sizes and shapes. Some are tall, some are small; some have large leaves, some have small leaves; and some have thorns while others do not. Yet the basic structures of all plants are the same. And each part has a special function. Understanding what each part does is important since people and their herds use plants. If their impact is too great, plants will be hurt.
Vocabulary
- Chlorophyll: A pigment which makes leaves green and facilitates photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis: the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy using carbon dioxide and water
Materials
- Notebooks and pencils
- A celery stalk
- Food coloring
Procedure
1. Using the background information above, explain the parts of a plant and what they do. Draw the parts of a plant on the board and have students copy them into their notebooks.
2. To show how water travels up the stem and into the leaves of the plant, take a stalk of celery and put it in a jar of water. Add a little food coloring to the water. Let it sit for a while and observe. The stalk and leaves should turn the color of the food coloring.
3. Some plants have silica on their leaves, similar to tiny pieces of glass. The silica discourages animals from eating the leaves. Have students taste a piece of cabbage and a piece of grass. How are they similar? How are they different? One is tasty and digestible, the other is not.
4. Discuss (and have students illustrate) the cycle of nature, the connection between plants and animals:
- What do plants get from the air? (carbon dioxide)
- How does carbon dioxide get into the air? (It is exhaled by people and animals.)
- What do animals get from the air? (oxygen)
- How does oxygen get into the air? (It is released by plants during photosynthesis.)
5. Discuss the many ways plants are used:
- Oxygen
- Food
- Shelter
- Fuel
- Medicine
