Lesson 2: Pollination
Additional Resources
Objective
- Students will understand the process of pollination.
Background
Plants that have flowers need to be pollinated in order to reproduce. Pollination is carried out with the help of animals or wind. Wind can blow pollen from one plant to another. Sometimes pollen sticks to animals as they gather nectar. When they go to another flower, some of the pollen is transferred from the stamen of the first flower to the stigma of the next one, and a seed is fertilized. The flower often has brightly colored petals and a strong scent to attract the pollinators.
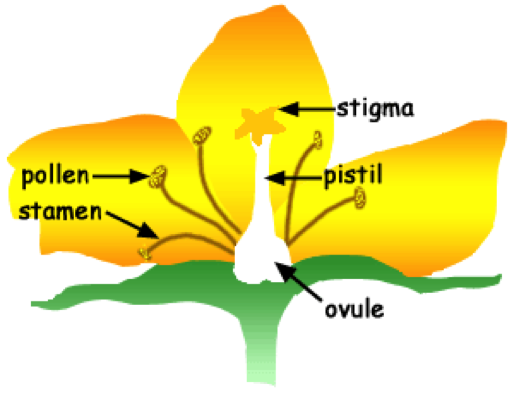
Vocabulary
- Pollination: the transfer of pollen from a stamen to a pistil
- Pollen: a fine powder produce by certain plants when they reproduce
- Stamen: the (male) part of a flower where pollen is produced
- Stigma: the tip of the (female) part of the flower that receives the male pollen grains
- Pistil: the (female) part of the flower that received the pollen
- Ovule: a minute structure that, after fertilization, becomes a plant seed
Materials
- Notebooks and pencils
- A pencil with an eraser on the end
Procedure
1.Using the background information above, explain pollination to the students. Draw the parts of the flower on the board and have students copy into their notebooks.
2. Using real plants and a pencil with an eraser, demonstrate how pollination takes place. Use the eraser to collect the pollen from the stamen and gently deposit it on the stigma. If plants can be brought into the classroom, watch them to see what happens.
