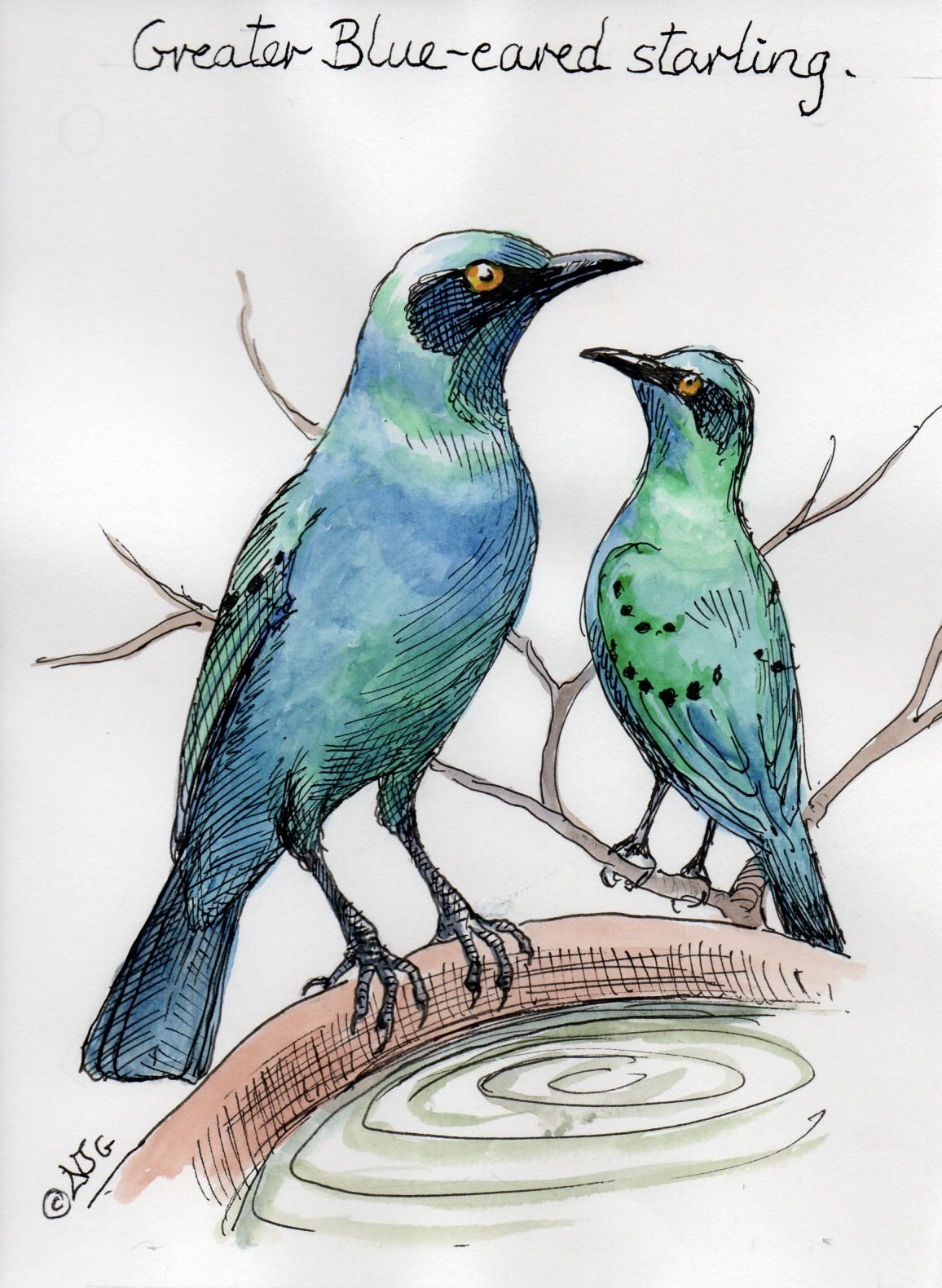
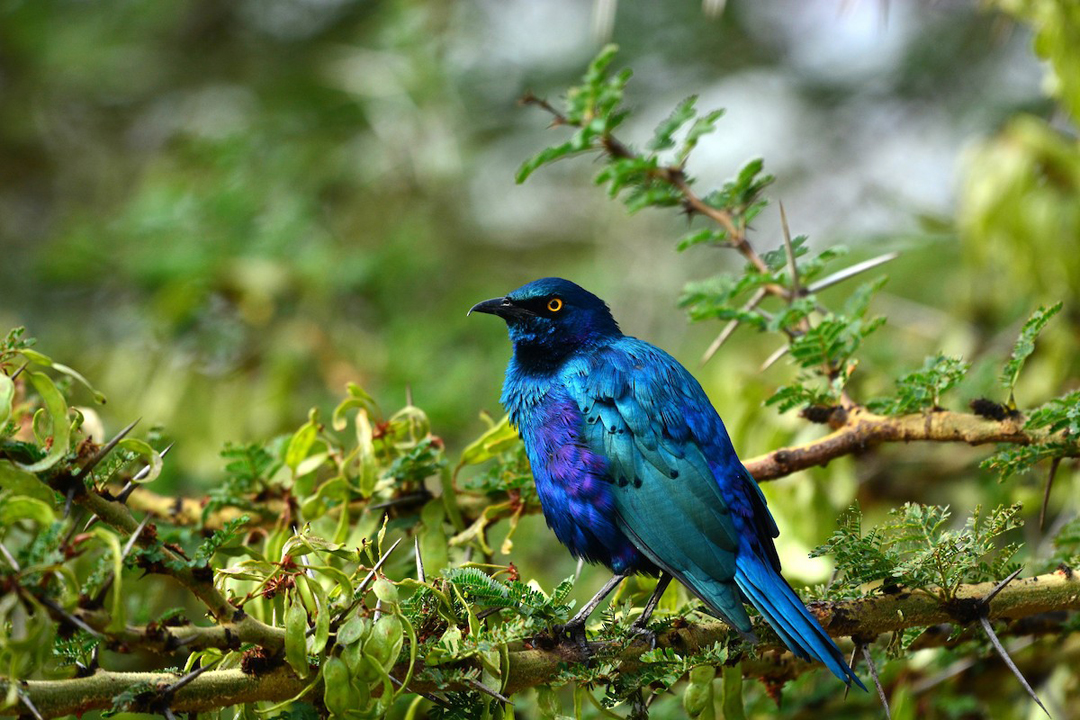
Social Structure
All starlings are known for their gregarious nature, and greater blue-eared starlings are no exception: more than 400 individuals form large roosts in reed beds, bushes, or thorn trees, and these gatherings often contain other starling species.
Communication
A range of songs and calls are often issued in a chorus from a tree where a group has gathered.
Behavior
These starlings forage for food by hopping on the ground. They also perch on the back of sheep, African buffalo, blue wildebeest, and Burchell’s zebra to search for invertebrate prey.
Conservation
Least concern
Diet
Greater blue-eared starlings primarily consume fruit and insects, as well as agave nectar and cereal grain.
Breeding
Monogamous pairs nest in holes in tree trunks excavated by other birds or created by natural causes; they sometimes line nests with grass, feathers, and other materials. Females incubate eggs, which hatch in about fourteen days, and both parents feed chicks.
Friends & Foes
Peregrine falcons may prey on these starlings, while great spotted cuckoos and greater honeyguides parasitize nests.
Population in Kenya
Greater blue-eared starlings are found more often on the west side of Kenya but can also be seen along the coastal belt.
Range & Habitat
These birds are found in an east-west band across sub-Saharan Africa as well as scattered throughout parts of southern Africa.
These starlings prefer dry savanna woodland as well as more humid woodlands and other cultivated areas and gardens.