Social Structure
Pied wagtails often call during their rising and falling flights. Urban dwelling birds gather at dusk, forming large roosts in city centers.
Communication
The pied wagtail’s call is a sharp chis-ick or seel-vit with an added chik. Its song is a twittering version of the call.
Behavior
Pied wagtails usually are seen in pairs, often around dam spillways and sewage works.
Conservation
Although no specific numbers are available for pied wagtails, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) considers their population to be stable in most parts of their range.
Diet
Pied wagtails feed mostly on insects, especially flies. They also eat grass seeds, tadpoles, worms, and small fish. Their adaptation to urban life has added cast-away bits of human food.
Breeding
Pied wagtails build a nest of grass and twigs lined with feathers. The female usually lays three to five eggs twice a year. Incubation lasts 11 to 13 days. Parents care for the chicks for three or four weeks after they fledge.
Population in Kenya
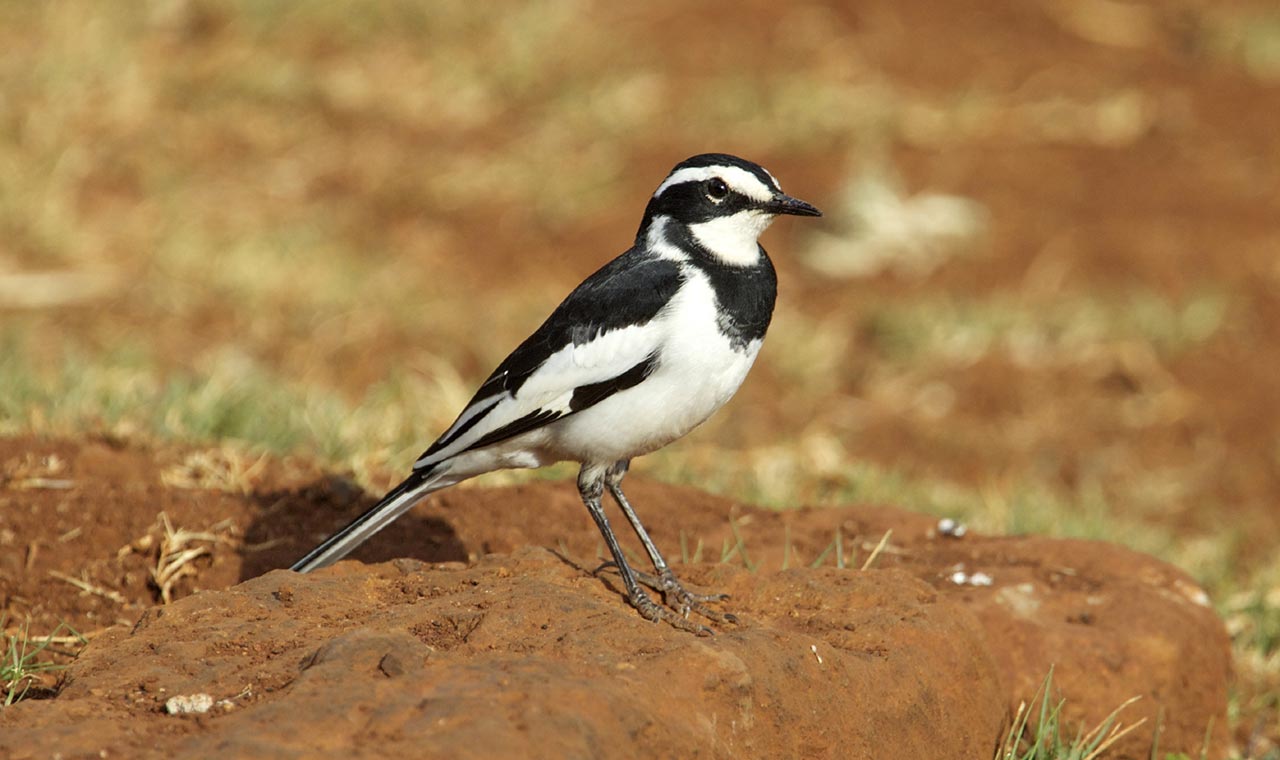
African pied wagtails live throughout southern and southwestern Kenya and are rarely seen in the northern and eastern regions.
Range & Habitat
African pied wagtails live in much of sub-Saharan Africa, from Senegal to Sudan and south to southern Africa. Although they prefer lakeshores and riverbanks away from humans, they are also found around urban sites, such as parks, golf courses, and gardens.