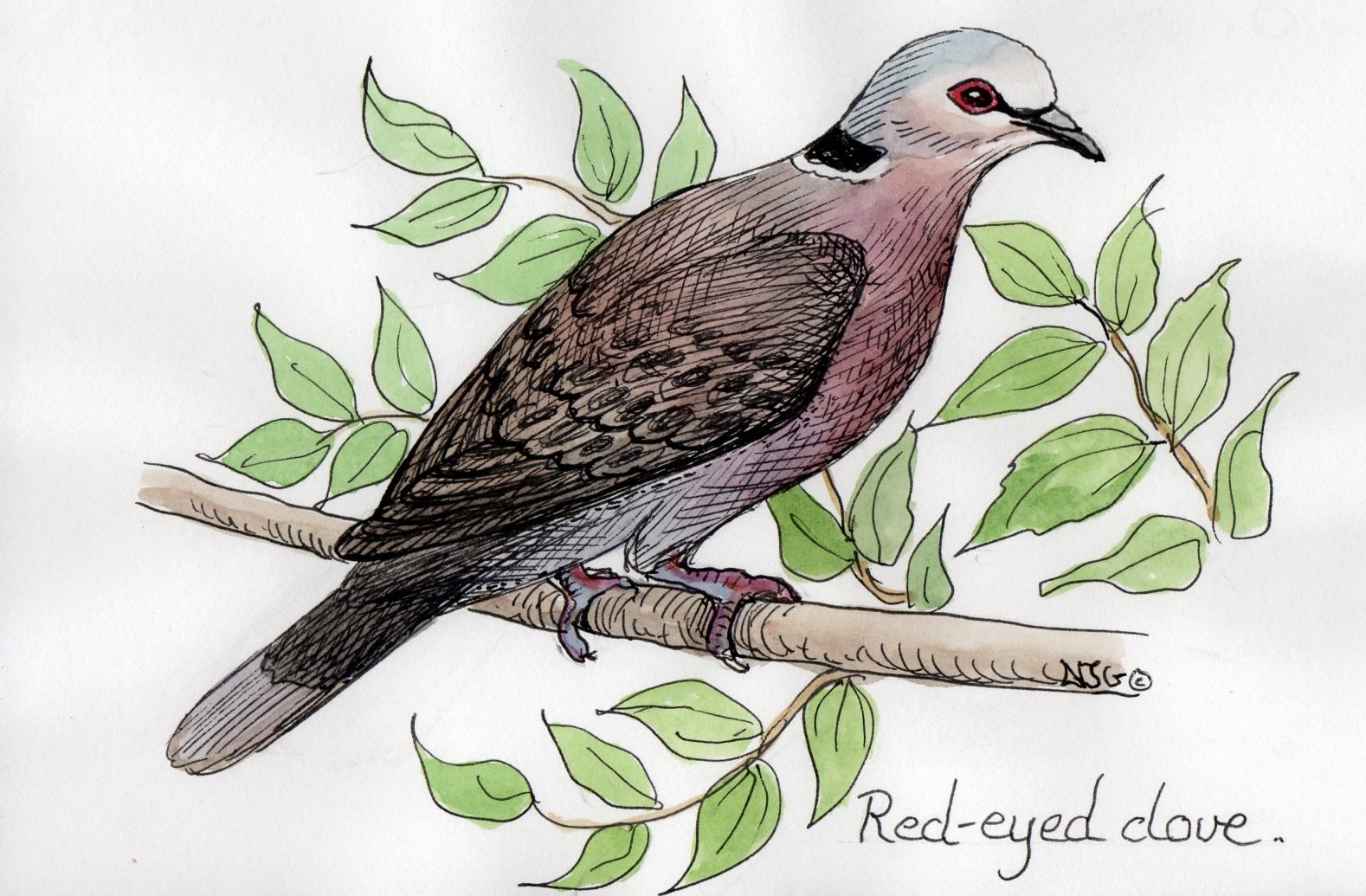
Social Structure
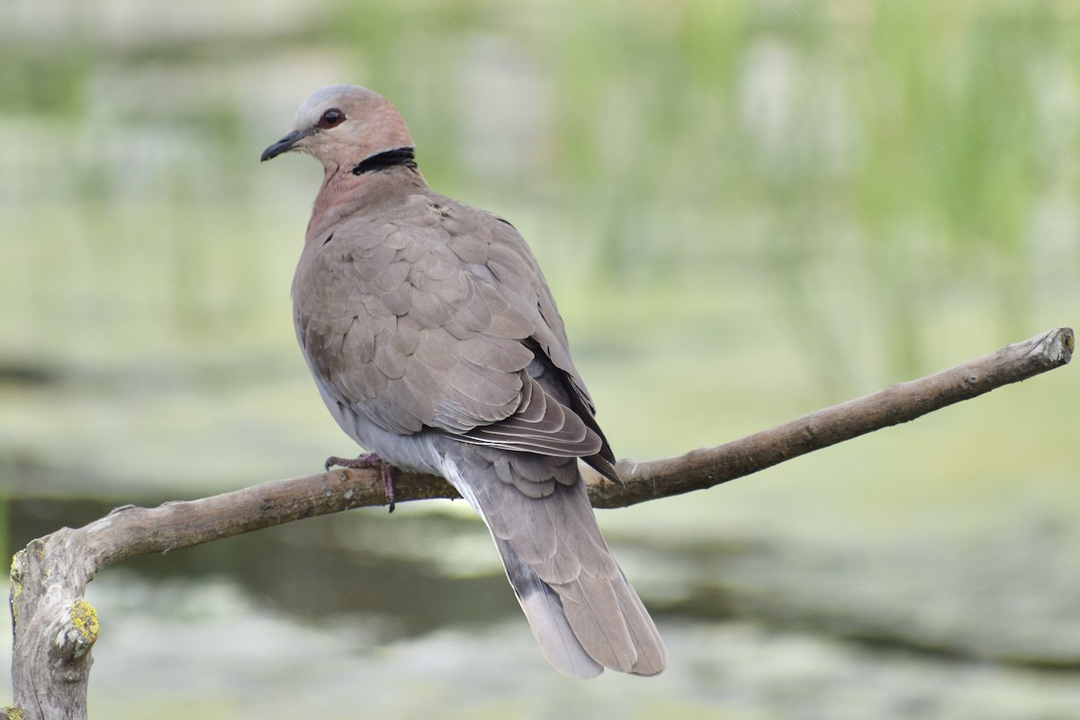
Similar to its relatives, red eyed doves usually keep to themselves or associate with a single other bird. However, it has been seen feeding in mixed groups with other doves.
Communication
Red eyed doves often call in a six-note pattern, emphasizing the final two notes.
Behavior
Red eyed doves usually forage on the ground, often under trees, and usually in the early morning and late afternoon. They call in the morning and at sunset, and have been heard on moonlit nights.
Conservation
Least concern
Diet
Red eye doves eat various seeds, including maize, sunflower, castor seed, and millet. They also consume berries and termites.
Breeding
Nests are constructed in trees or other vegetation, and are made of twigs and grass, although sometimes red-eyed doves use crow, thrush, or egret nests instead. Broods consist of one or two eggs that both parents incubate for around two weeks, and chicks leave the nest around two to three weeks after they hatch.
Friends & Foes
Pythons, sparrowhawks, and falcons all prey on red-eyed doves.
Population in Kenya
It is common in most habitats.
Range & Habitat
Red-eyed doves are found throughout much of sub-Saharan Africa and along the southwest Arabian Peninsula.
Red-eyed doves are found almost everywhere except deserts, and favor access to large trees and water. They frequent parks and gardens and have become habituated to living in human environments.