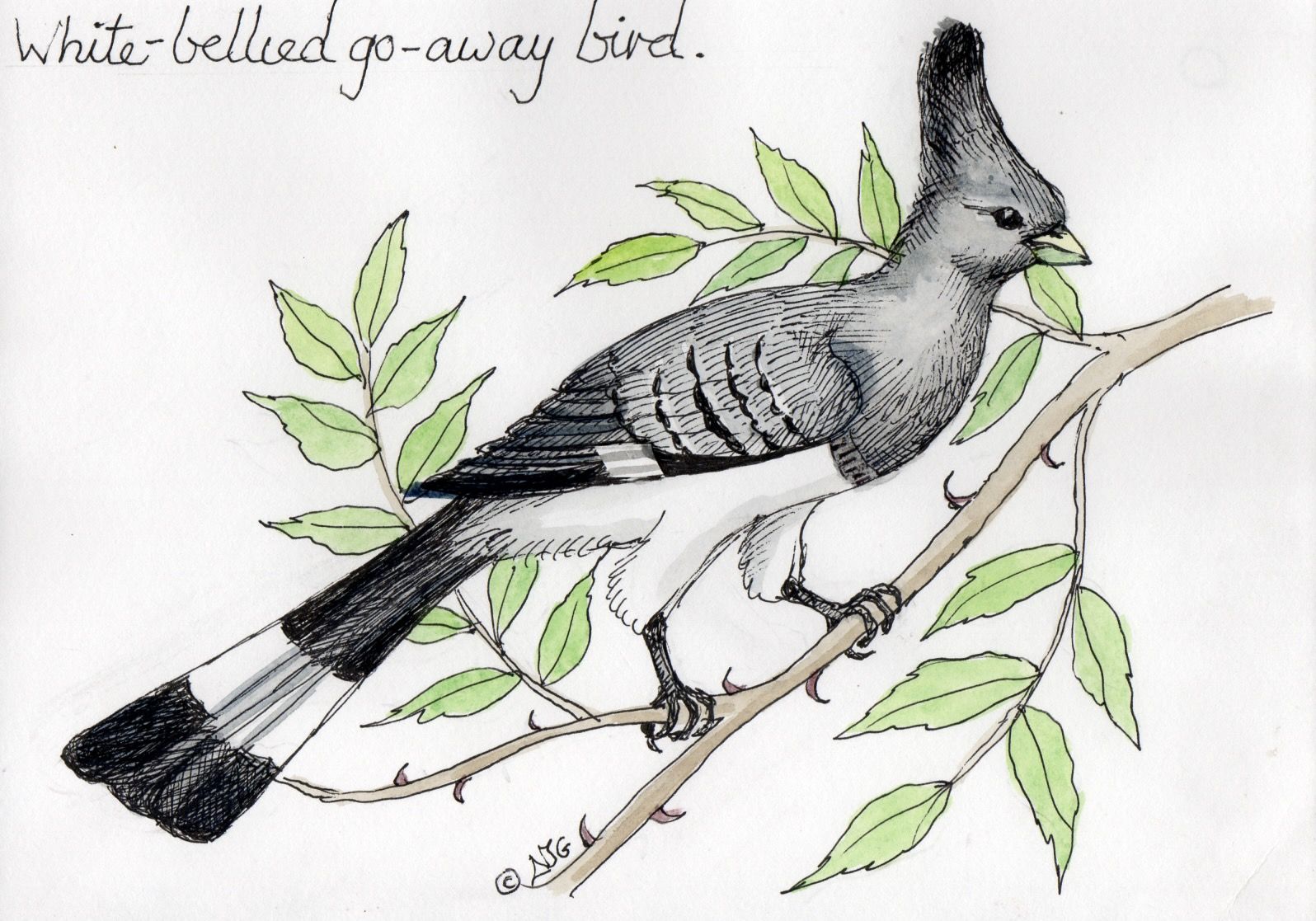
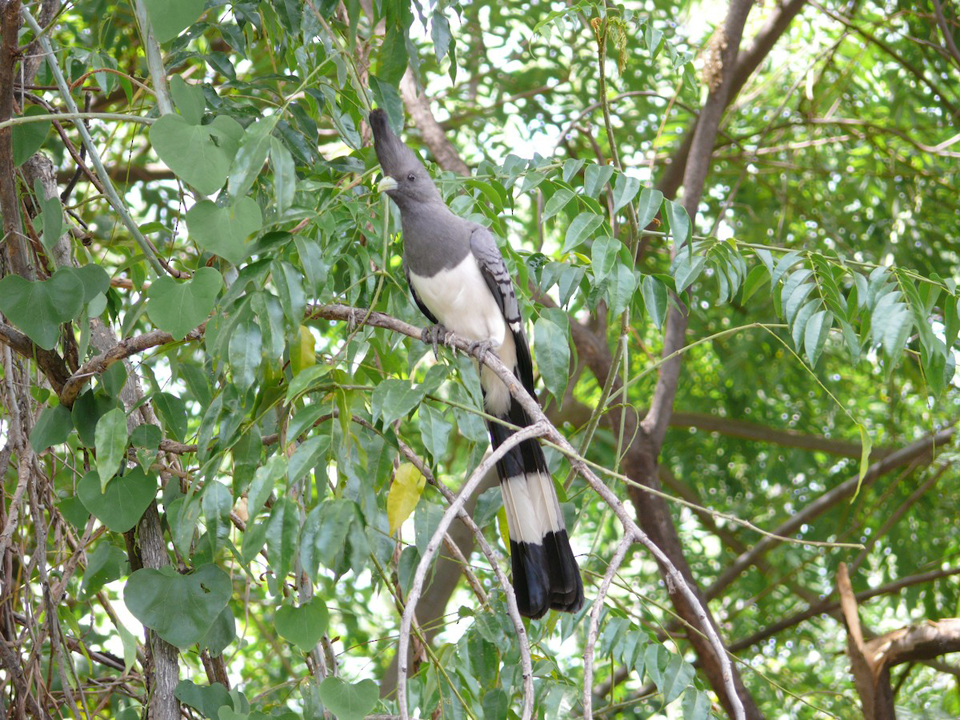
Social Structure
These birds gather in pairs or small family groups, or can be found alone.
Communication
Their loud and distinct “gorrwaaay” call gave rise to their name.
Behavior
Territorial and restless, groups call loudly to each other as they fly from tree to tree. They are adept climbers among branches and vines.
Conservation
Least concern
Diet
White-bellied go-away birds consume fruit, flowers, and acacia seeds and buds, as well as some invertebrates.
Breeding
After a vigorous courtship, monogamous pairs build a frail nest in acacia-type trees. Both parents incubate the eggs and help feed chicks, which hatch after around a month and fledge 4-5 weeks afterwards.
Friends & Foes
Birds of prey, monkeys, and snakes can all threaten white-bellied go-away birds.
Population in Kenya
The white-bellied go-away bird is common in much of Kenya.
Range & Habitat
These birds are found in some parts of east and northeast Africa.
White-bellied go-away birds favor acacia steppe and savannas.