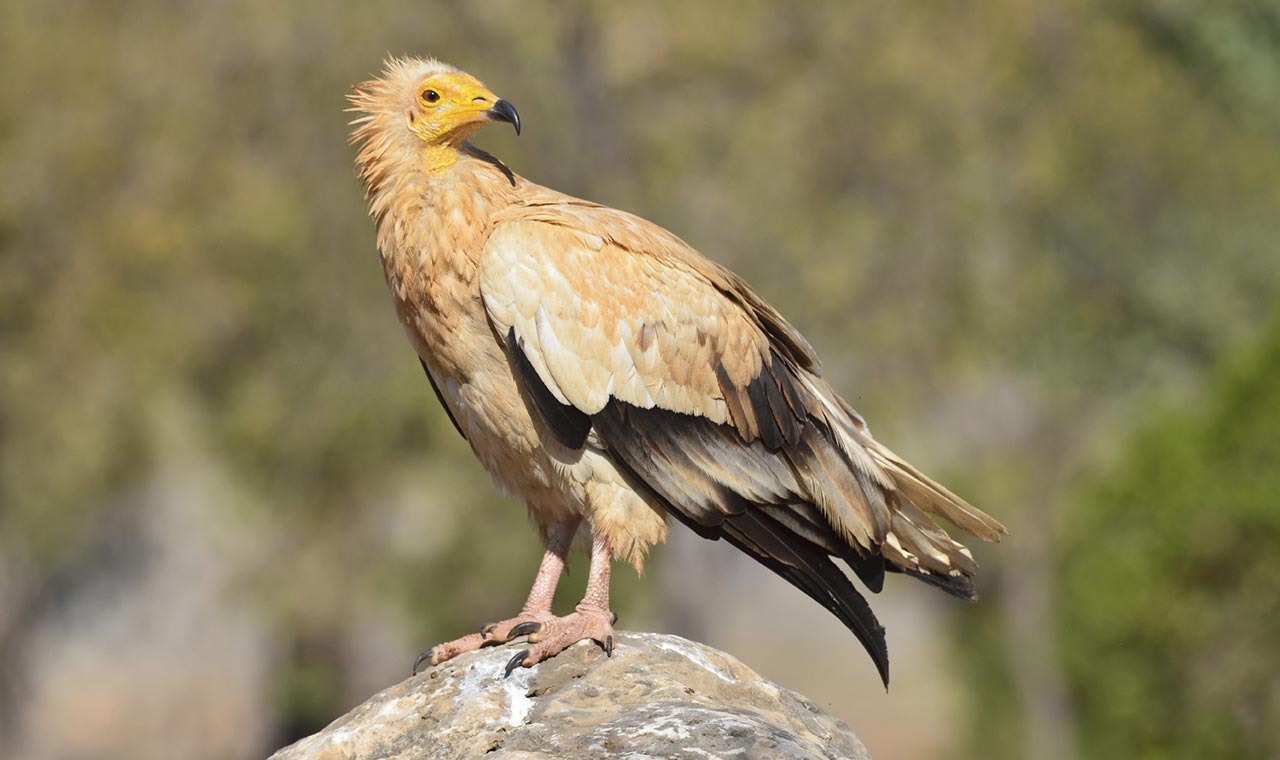
Social Structure
Although normally seen alone or in pairs, Egyptian vultures are also found in family groups.
Behavior
Egyptian vultures have great stamina and can fly almost 45 miles (70 km) in their daily search for food.
Diet
Egyptian vultures feed mostly on carcasses of birds and small mammals. They usually hold back until the bigger vultures and ravens finish dining. They sometimes hunt live small mammals, reptiles, and birds. This vulture is one of the few birds that are tool users. It will pick up a stone in its slim bill and toss it at an ostrich egg until it cracks open and yields a feast.
Breeding
Egyptian vultures build nests of shrub branches and bones in clefts of rocky cliffs. The two eggs hatch in 42 days and are fed regurgitated meals by their parents for about three months. After that, the chicks start looking for food with their parents. Breeding pairs may return to the same nesting site for many years.
Friends & Foes
Farmers put out poisoned carcasses to kill marauding lions, and vultures die when they feed on these corpses. Another threat to vultures comes from remains of cattle that have been fed antibiotics that are deadly to vultures. Such secondary poisonings have reduced vulture populations over many parts of Africa to the point that the Egyptian vulture is now considered endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Population in Kenya
The Egyptian vulture, one of seven vulture species living in Kenya, is found mostly in protected areas, including Wider Tsavo East and West National Parks.
Range & Habitat
Most Egyptian vultures are found in Ethiopia, East Africa, Arabia, and India, with smaller populations in Algeria, Niger, northernmost Cameroon, Chad, and northern Sudan. They also inhabit the Canary and Cape Verde Islands and southern Europe. Egyptian vultures prefer arid, semiarid, and bush habitats from near sea level to 9,800 feet (3,000 m).