Social Structure
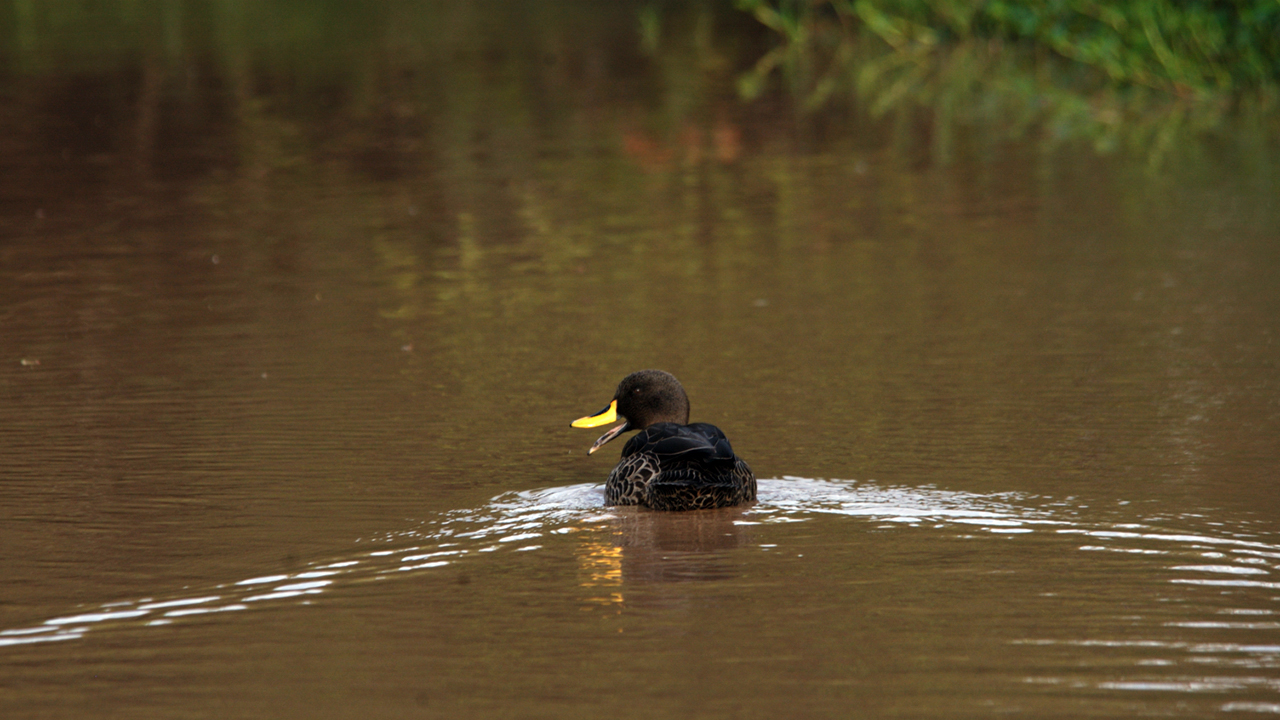
Yellow-billed ducks are highly social birds and form large populations during the dry season. As soon as the rains come, they disperse to breeding areas.
Communication
Male yellow-bills utter low whistles; females produce a deepening series of hoarse quacks.
Behavior
Yellow-billed ducks usually stay in one location. But those that live in southern Africa are nomadic, moving from place to place within a local area. Yellow-billed ducks usually forage at twilight and night. During the day, they tend to be sedentary.
Conservation
Despite being hunted by humans, populations of yellow-billed ducks are mostly stable and in some areas even increasing.
Diet
Yellow-billed ducks are omnivorous. Their diet includes the fruits, seeds, roots, leaves, and stems of aquatic and terrestrial plants; insects, such as mayflies, water beetles, and grasshoppers; and crustaceans, mollusks, and agricultural grains, such as maize and sunflower seeds.
Breeding
After an elaborate courtship, pairs of birds select sites that are hidden by tall plants and other vegetation to build their ground nests. They use grass, rushes, and reed stems and line the nest with down. The female lays 4 to 12 eggs and incubates them for 26 to 29 days. The chicks fledge in 68 days but usually stay with their mother for another six weeks.
Friends & Foes
In some parts of their range, yellow-bills interbreed with mallard ducks. They are preyed upon by black-backed jackals and tawny eagles.
Population in Kenya
Yellow-billed ducks are found in freshwater sites in the highlands of southwestern Kenya at elevations of 5,250 to 9,840 feet (1,600 to 3,000 m).
Range & Habitat
Yellow-billed ducks range from Ethiopia and Sudan to South Africa.